
- #Use tcpview check monitoring install
- #Use tcpview check monitoring update
- #Use tcpview check monitoring trial
- #Use tcpview check monitoring download
- #Use tcpview check monitoring windows
Trial of the program you pick from the list above.
#Use tcpview check monitoring install
Tip: It’s recommended to install the free You can do so by running in a Dos box the tcpvcon using this syntax: tcpvcon > filename.txtĪ file called “filename.txt” will be created and you’ll have the connection info available for a later check.Be alerted each time the program finds a breach, and you can usually eitherĮnable a block to prevent it from happening again or you’ll be told that theĮxample, if a keylogger has been sending your keystrokes to a hacker in anotherĬountry, the anti-spyware tool will likely block it and then tell you so. I would recommend to save the output in a text file so you’ll be able to review it easily. But its default output it’s clearer than netstat. With tcpvcon you cannot kill any process, just see the opened ports/connections. Only show endpoints owned by the process specified Show all endpoints (default is to show established TCP connections)
#Use tcpview check monitoring windows
Tcpvcon usage is similar to that of the built-in Windows netstat utility: TCPView includes Tcpvcon, a command-line version with the same functionality (basically a more clear to read Netstat with fewer options. You can also save TCPView’s output window to a file using the “ Save” icon. You may discover that something is keeping opened some strange port… If this option is enabled, you’ll see not only the existing connections, but you’ll be able to see which ports are open on your system. In this case, you’ll have to do the Whois manually, then…įor troubleshooting purposes you should consider enabling the option” Show Unconnected Endpoints” under the Options menu (or by pressing Ctrl+U). Please note that I’ve noticed that if you are using a Proxy Server or VPN connection, the Whois option is not available. If you want to have more info on the remote server, click choose this option and TCPView will search on the Internet the Whois information. When you right click on a process/connection, you’ll see a small menu that will give you the option to Kill the process or Close the connection.Īnother option you can appreciate in the context menu is “ Whois”. If you just close the connection, there is a good chance that the process will be in a “responding” state again and you’ll not lose data as it would happen if you would have closed the process instead. Sometimes it’s good to close a connection, not because it’s a Virus/Trojan that is opening it, but because an application can go to a “Not Responding” state when is waiting for incoming data from a network source that is a not reliable or that is taking too long to answer. This means that if you can identify some strange process connecting to something strange, you can close this connection and monitor the process to see if it keeps opening the connection again, until you may decide that is the time to kill the process. TCPView offers two interesting functions out of the box:
#Use tcpview check monitoring update
On Windows XP systems (or higher), TCPView shows the name of the process that owns each endpoint.Īs explained in the brief instructions that come with the application, TCPView updates every second, but you can use the Options -> Refresh Rate menu item to choose a different time (1, 2, 5 seconds or paused).Įndpoints that change state from one update to the next are highlighted in yellow and those that are deleted are shown in red. You can use a toolbar button or menu item to toggle the display of resolved names ( Options -> Resolve Addresses).
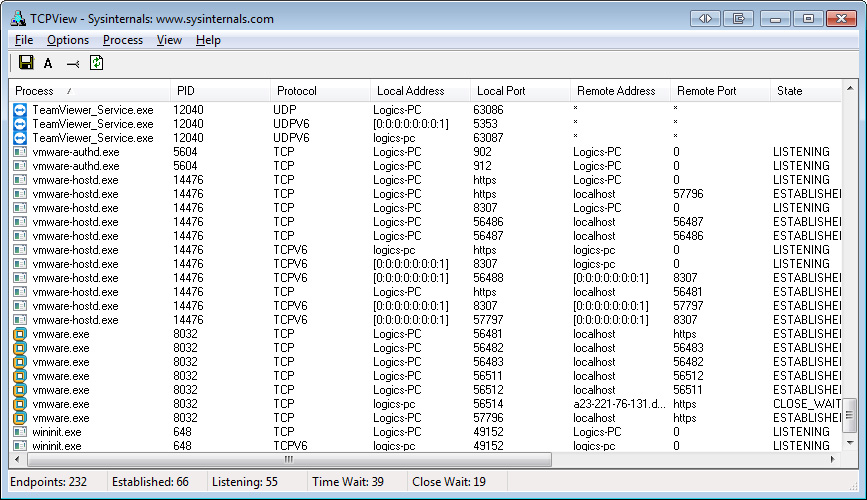
When you start TCPView it will enumerate all active TCP and UDP endpoints, resolving all IP addresses to their domain name versions. Starting from Windows XP (and moving through Vista, 7 or Server 2008) TCPView also reports the name of the process that owns the connection.
#Use tcpview check monitoring download
You can download the latest version from This is a free program that shows you a detailed listings of all TCP and UDP endpoints exactly as Netstat would do, but in a clear and easy-to-read graphical interface.Īll the local and remote addresses endpoints and the state of TCP connections is displayed.
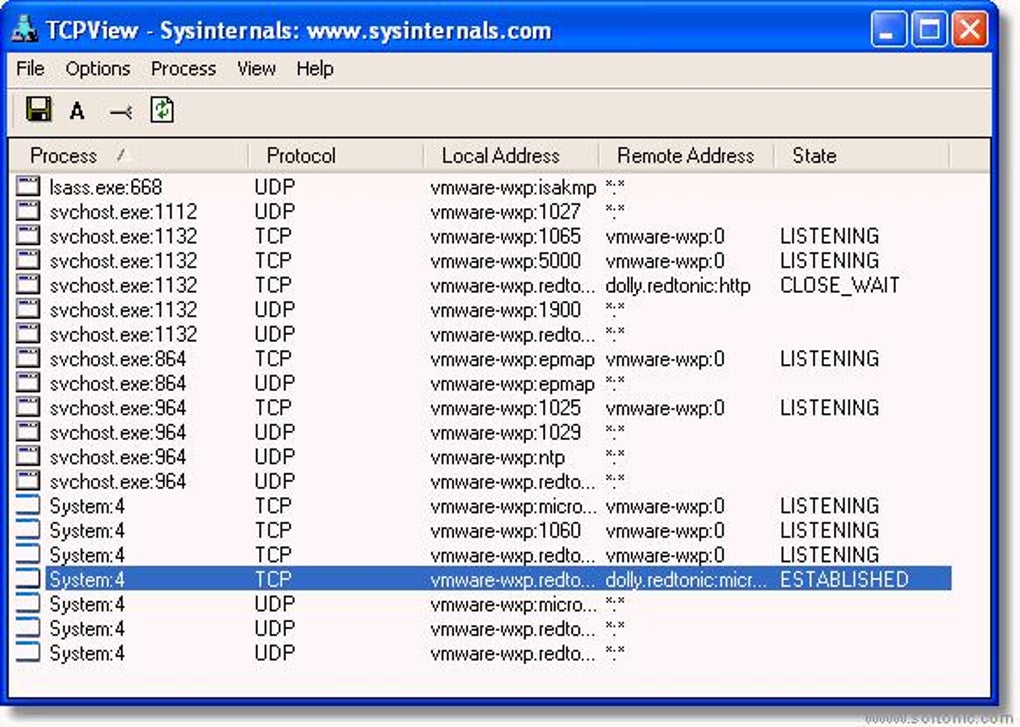
That’s why the Sysinternals team at Microsoft has created TCPView. However its output is an old-style, text only list of connections, so it can be hard to use or clearly understand its content. Microsoft Windows is shipped with the command line utility Netstat that is commonly used to list all the connections opened on a machine and troubleshoot them. Where is connecting your machine? Are all the connections legitimate? Is somebody connecting to your machine? It’s very important to know about the various open TCP and UDP connections as some of them can be the clear indication that some Trojan is using your connection or that maybe somebody is trying to access your system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
